Plating techniques
Electrochemical (electrolytic) surface treatment
The most commonly used coating method, which requires the object to be electrically conductive. The coating thicknesses vary from 0.1 µm to 60 µm, depending on the coating and application.
Chemical surface treatment
A method that is also suitable for non-conductive objects. The most commonly used chemical coatings are nickel and copper. The advantage of the method is the even thickness of the coating and good penetration.
Selective coating
A method used when you want to coat only certain section of a part. Selective coating can also be applied in vacuum evaporation.
Brush plating
An electrochemical method in which the plated part is not immersed in a coating electrolyte. The brush plating is a good solution especially for applications, where the coating has to take place on site (e.g. on a power plant) or it is not desired to coat the part throughout.
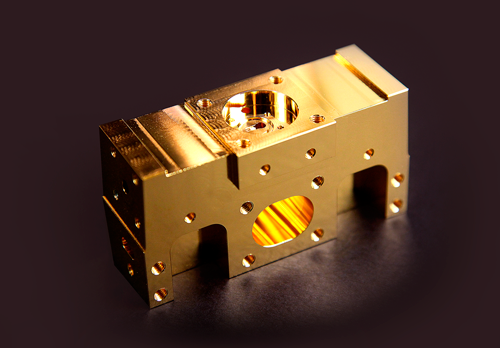
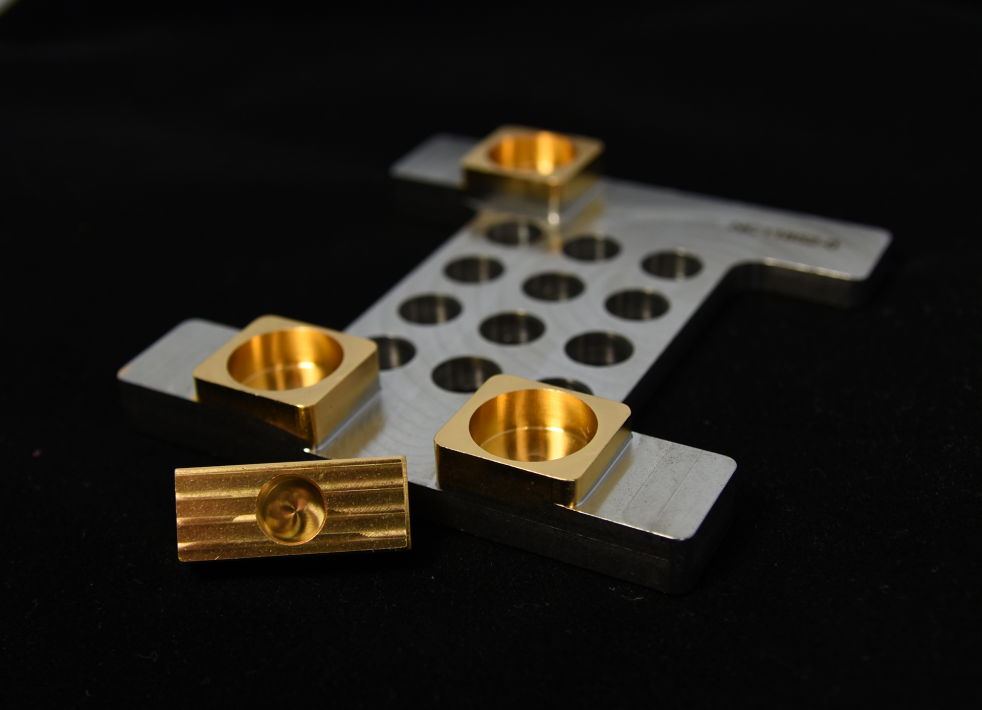 Brush plated part
Brush plated part

